Introduction
There has been a lot of excitement about self-driving vehicles since the beginning of the twenty-first century. Maybe you're one of the many who believe in the future of automated vehicles, with improved safety on the road as well as personal time spent behind the steering wheel, and relief from the burden of driving.
You can better prepare in the near future, by understanding the way self-driving vehicles function. Self-driving vehicles rely on sensors, computers and algorithms, machine learning and artificial intelligence in order to precisely perceive and securely navigate their surroundings.
This article focuses on the intricate sensors you'll find AI In Automotive Industry. Let's look at the technology that allow self-driving vehicles to be built.
Self-driving Cars Use Sensors to Work
Just like humans, self-driving vehicles need to detect their surroundings in order to safely navigate. The human body uses senses such as hearing and sight, taste as well as smell and touch to communicate with their surroundings. Autonomous car technology designers provide autonomous vehicles with advanced sensors to detect analogy.
Illuminating the World With Lidar
The Lidar (light detection and range) which is often referred to by the name of 3D scans, are a device used by self-driving vehicles to analyze their surroundings using lasers. The typical lidar sensor sends thousands of laser beams of infrared light onto its surroundings and waits for those laser beams to bounce off the surrounding elements. Numerous pulses result in points clouds (sets composed of numbers that represent three-dimensional forms that are space-based) made of laser light.
Lidar systems monitor the length of time it takes to generate an optical signal and detect the beam of light reflecting off of a physical surface on its photodetectors. Lidar utilizes laser speed and speed-of-light to determine distances between objects. In the longer time it will take the lidar photodetector to get an incoming light signal the further away the object is. Lidar systems allow autonomous vehicles to identify small objects with accuracy. But, they are typically not reliable at night or in severe weather conditions.
Reading the Environment With Radar
Radiar (radio detection and the ability to range) is an effective tool in numerous situations, such as forecasting weather communications, astronomy, maritime navigation, military operations as well as autonomous driving.
Autonomous vehicles can radiate radio frequencies in well-known directions, using radar transmitters. Reflections of the waves back to the radar receiver of a car aid in obtaining details about the environment, including angles, distances, and speeds. Radar is typically effective for long distances and the majority of weather conditions. However, it's not very efficient for identifying objects, and can be a false identification of objects.
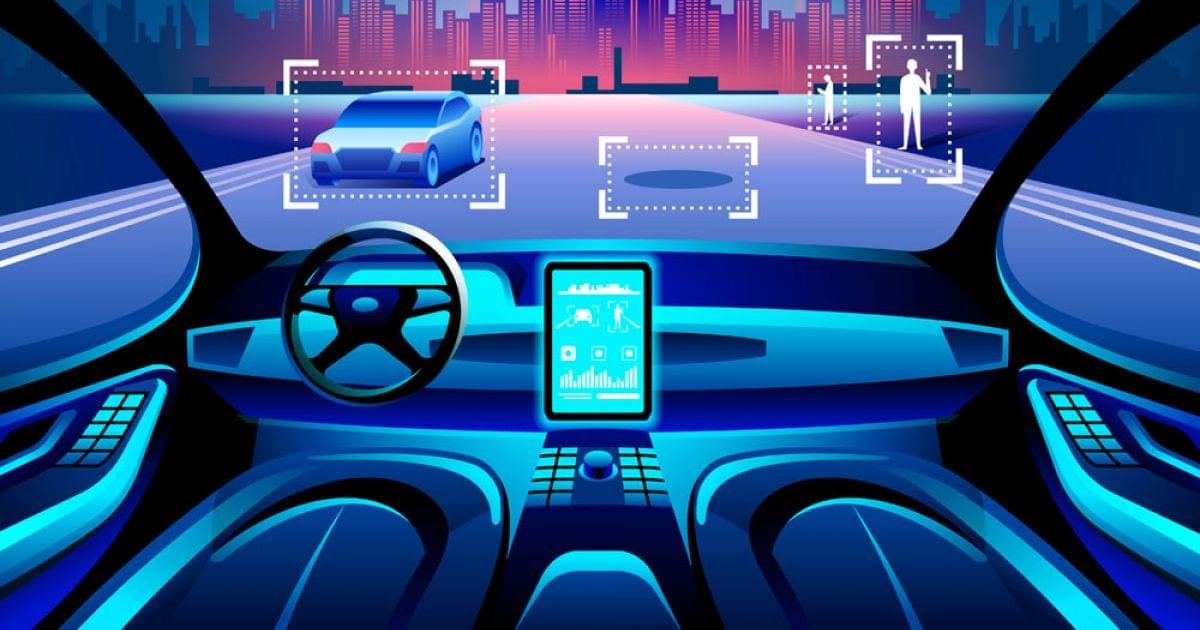

Hearing With Sonar
Sonar is a method used by autonomous vehicles (sound navigation and the ability to range) to communicate with objects and to navigate. Sonar is either active or passive. Systems that passively detect sounds produced by objects that are close to. Systems that emit active sonar emit waves and read echoes that are returned by physical surfaces.
Self-driving vehicles can utilize sonar sensors to detect massive objects composed of solid material (e.g. ceramic, metal) at shorter distances. Sonar sensors do not require light in order to function. But, sonar sensors are limited in their speed by sound (which is slower than light) and may falsely detect objects that aren't present.
Capturing Images With Cameras
Autonomous vehicles are able to visualize their surroundings with high-resolution camera images. Autonomous cars can utilize photographs from cameras in order in order to "see" and interpret environmental specifics (e.g. traffic lights, signs or wildlife) using methods that are similar to humans' vision (aka computer vision).
Autonomous vehicles can make use of a variety of kinds of input data in computer vision. Examples include:
- Multi-dimensional data derived from 3D scanners
- Video segments
- Camera images that are captured from various perspectives
Self-driving vehicles can detect objects, regulate vehicle motion and create 3D scenes by using images.
Similar to other sensor systems, cameras have their strengths and weaknesses. Image data Collection provide advantages with high-resolution images, but they don't work in every weather type. Additionally, cameras can only capture visual information that is visible.
Sensing Movements With Inertial Navigation Systems
Inertial navigation systems, such as the inertial measurement unit (IMUs) (e.g. accelerometers and accelerometers, and gyroscopes) detect the car's physical movement. These devices aid in helping self-driving vehicles to stabilize themselves. They aid in determining if they are required to take any form precautionary safety measures (e.g. install an airbag, stop the car from colliding with the road).
Tracking Positions With the Global Positioning System
The U.S. owns a 24-satellite-based radio navigation system known as "the Global Positioning System (GPS). People who have the GPS receiver are able to obtain data on time and geolocation.
Self-driving vehicles can make use of GPS to pinpoint their location using numeric coordinates (e.g. latitude and longitude,) which represent their physical location in the world. They also can navigate by using real-time GPS coordinates along with other map data (e.g. through Google Maps). GPS data can vary around five meters. To correct for the ambiguity of GPS data, autonomous vehicles utilize unique methods of data processing, such as particle filters to increase the accuracy of location.
Making Good Use of Sensors
Self-driving vehicles typically have a variety of sensors that have redundant and overlapping functions. This is why they have sensors that can be used as backup (in the event that one sensor fails the other one will function) and take advantage of the benefits of various sensors.
Autonomous vehicle developers employ innovative data-processing methods such as sensors fusion to process AI Training Dataset from multiple sensors in real-time. Sensor fusion is a way to enhance the way self-driving vehicles perceive and react to environmental conditions and improve the safety of cars.
Getting Around in Self-driving Cars
Artificially intelligent technology self-driving vehicles function as humans do to get from one point to B. Also, just like human beings, self-driving vehicles employ basic navigational skills.
maps and read. Self-driving cars combine the sensor data they collect along with other information (e.g. electronic maps) to make and read maps of their environment.
Planned Path. Artificially intelligent autonomous vehicles make use of sensors to determine routes they can take through their surroundings.
Obstruction Avoidance. Self-driving cars use their sensors in real-time to ensure safety. For them to be able to drive, they have to precisely detect, interpret, and react to any environmental signals to avoid obstacles such as cyclists, pedestrians as well as other vehicles.

GTS And Automotive Industry
We at Global Technology Solutions have spent more than half-decade developing and perfecting our automotive skills. We have active partnerships with reputable suppliers and OEMs, as well as multilingual assistance. With our services of car datasets and traffic life datasets, GTS has a team of specialists and the relevant resources on the ground to help you improve your product development and testing workflow. We specialize in data collection and annotation along with Audio data Transcription Services and OCR Datasets and our clients are of a wide variety.
